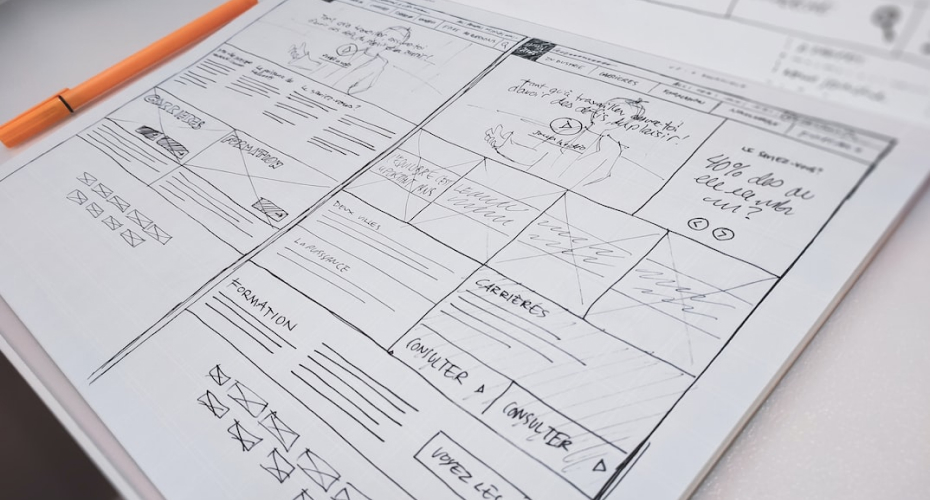
To establish the structure and flow of potential design solutions, designers use a process called “wireframing” to create overviews of interactive products. This process allows all stakeholders to agree on where the information will be placed before the developers build the interface out with code.
Depending on the level of detail needed, wireframes might be manually drawn or digitally constructed. A wireframe is stripping the idea down (such as an app or a webpage) down to its very core. Wireframes provide a clear overview of the page structure, layout, information architecture, user flow, functionality, and intended behaviors.
Since building a wireframe doesn’t take much time, simplicity is the main concern here. The user experience or the level of engagement are not your main concerns here. As a wireframe usually represents the initial product concept, styling, color, and graphics are kept to a minimum.
Effective wireframes serve as the skeletons of strong prototypes and delightful designs
To swiftly decide whether concepts are worth developing, your team and stakeholders need to be able to quickly evaluate realistic-looking, lean layouts that you create through effective wireframing.
In order to quickly communicate an idea, you can create a low-fidelity wireframe. By doing wireframing effectively, you may protect yourself, your team, and your company from pursuing subpar solutions.
What Does A Wireframe Look Like?
- Most wireframes are grayscale or in black and white.
- To accommodate content, divide the screen into big blocks.
- High-fidelity wireframes boast pixel-specific layouts.
- Using a straightforward box in place of images
- Lorem ipsum text is common as a placeholder
- Wireframing is a practice most commonly used in UX design by UX designers.
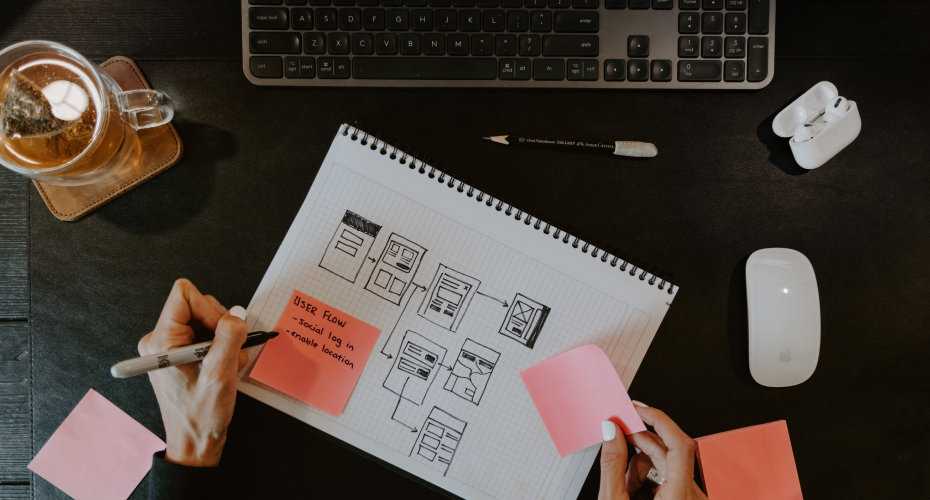

What is the purpose of wireframing
They maintain the user-centricity of the concept, make website functionality clear and comprehensible, and are easy to make quickly and affordably.
Wireframes keep the concept user-focused
Wireframing is the perfect way for the designers to gauge how the user would interact with the interface. They help users provide feedback, start interactions with stakeholders, and spark creative ideas among designers.
These observations assist the designer in creating items that are cosy and simple to use by enabling them to comprehend what the consumer perceives as intuitive.
Wireframes clarify and define website features
By wireframing a particular feature, you can explain to your clients exactly how it will work and what it will be used for. With high-fidelity wireframing, you may add more realism by integrating images and possibly even some interactivity.
Wireframes are quick and cheap to create
You may also create a digital wireframe in a matter of minutes thanks to the number of tools available. Changes are more difficult to make the later they are made in the product design process!
What Is Prototyping?
A high-fidelity version called a prototype may not differ significantly from your finished product in terms of appearance and behavior’s, depending on user feedback.
Design sprints and design thinking both have a fourth phase, which is prototyping. It’s a crucial component of user experience (UX) design that typically follows ideation, when you and your team have produced and chosen ideas that can satisfy the needs of users.
Prototypes are great for user testing. You can test out the interactions, the user experience, the usability, and the user interface.
In the Design Thinking process, prototyping is a crucial step that is frequently applied during the final testing stage. Prototyping allows you to build simple, small-scale prototypes of your products, and use them to observe, record, and assess user performance levels or the users’ general behavior and reactions to the overall design.
Types of Prototyping
Prototyping techniques that are frequently used include:
- Sketches and Diagrams – Use sketches to begin the process of conceptualizing and building a new product and share the concept with teammates for more ideas and discussions.
- Paper Interface – Paper interfaces prove to be handy for early-stage prototyping for digital products.
- Storyboards – Storyboarding is an excellent way of telling stories and guiding targeted customers through a user experience.
- Role-Playing – Role-playing or experiential prototyping enables designers to explore situations within the system that you’re targeting physically.
- Physical Models –Physical models are often built using paper, cardboard, clay, foam, or by repurposing existing objects.
- Wizard of Oz Prototypes – The term “Wizard of Oz Prototypes” refers to prototypes having fictitious functions that can be used to test consumers.
The advantages of prototyping are that you:
- Ensure that all those involved feel a feeling of ownership
- Reduce the number of faults that must be fixed prior to the introduction of the product to shorten time-to-market.
- Participate in user feedback and assist with repeated testing
- Detect errors earlier and save time and money.
- Enhance collaboration within your team members internal
Author
Jayesh Patel
Jayesh Patel is a Professional Web Developer & Designer and the Founder of InCreativeWeb.
As a highly Creative Web/Graphic/UI Designer - Front End / PHP / WordPress / Shopify Developer, with 14+ years of experience, he also provide complete solution from SEO to Digital Marketing. The passion he has for his work, his dedication, and ability to make quick, decisive decisions set him apart from the rest.
His first priority is to create a website with Complete SEO + Speed Up + WordPress Security Code of standards.